
What if you could eat steak and fruit and still achieve optimal health and performance?
Many diets overcomplicate nutrition, cutting out entire food groups or relying on processed, artificial foods that leave people feeling sluggish and deprived.
Strict, low-carb, or high-protein approaches can work for some.
Still, they often lack the balance needed for long-term sustainability.
The fruit and meat diet offers a simple, whole-food approach that gives high-quality protein, good fats, and easily digestible carbohydrates.
By focusing on nutrient-dense animal foods and natural fruit sugars, this diet helps with muscle gain, fat loss, digestion, and overall energy.
It takes the best of the carnivore diet and adds natural carbohydrates for those who thrive with a bit more fuel.
This book breaks down everything you need to know about the meat and fruit diet.
Whether you are an athlete, a bodybuilder, or just looking for a simple and effective way to eat, this diet may be a life-changer to your health.
Key Takeaways
What Is the Meat and Fruit Diet?
The meat and fruit diet is a simple yet effective method focusing on whole, unprocessed animal foods and natural fruits.
Many people consider this diet a flexible alternative to strict carnivore, keto, or paleo approaches.
I personally tried the meat and fruit diet for two weeks, and the changes were noticeable almost immediately.
My digestion felt lighter, my energy remained steady throughout the day, and I didn’t experience the sluggishness I sometimes get from a zero-carb approach.
The combination of protein, healthy fats, and natural sugars kept me full while allowing for variety and better workout recovery.
Unlike stricter plans, I found maintaining them easier without feeling overly restricted.
You can watch this video with self-experiment and results on the meat and fruit diet.
How It Compares to Other Diets
This diet is based on the ancestors’ diet and adheres to its characteristics in keto, carnivore, and paleo diets.
A comparison of how they are different and similar is illustrated below:
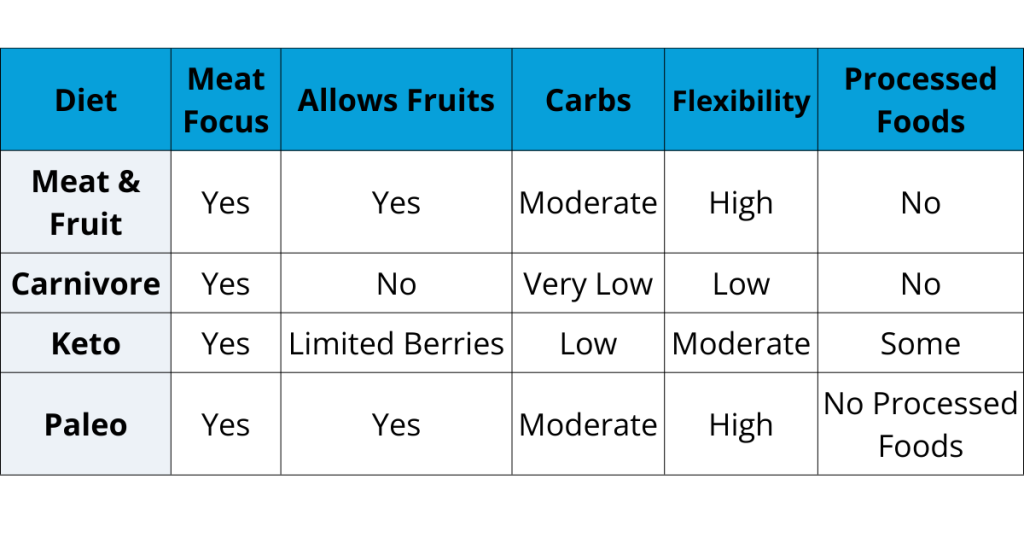
The most divergence is in carbohydrate intake. Where the carnivore diets exclude carbs, the meat and fruit protocol reinstates them to their natural form.
Keto only allows small servings of fruit, normally in berry form, since they are less sweet.
Paleo offers meat and fruit but not dairy products and processed foods.
The meat and fruit regimen is also a less strict program than a hardcore carnivore diet.
A dirty carnivore may have processed food or dairy on the plate, whereas the meat and fruit way is about consuming whole, intact foods.
The regimen is at a mid-point between consuming low-carb and whole food and ought to be easier to adhere to for people who don’t do long-term carb-reducing but still don’t enjoy processed foods.
The majority of people choose the meat and fruit diet because it is easy, nutritious, and flexible.
It provides stable energy, supports muscle retention and fat reduction, and is easy to adjust based on personal needs.
READ MORE: Carnivore Diet and Fasting: Transform Your Metabolism
Health Benefits of the Meat and Fruit Diet
The fruit and meat diet offers a whole-food, nutrient-dense approach that is supportive of muscle gain, digestive health, and overall health.(1)
By emphasizing natural carbohydrates and high-quality animal foods, the diet helps support stable energy levels, the minimization of inflammation, and improved body composition.
Many people notice tangible health benefits, including better digestion, weight loss, and improved endurance.
Expert Insight: Whole-food diets that combine high-quality protein with natural carbohydrates can enhance metabolic function, stabilize blood sugar, and reduce oxidative stress, contributing to long-term health and performance.(2)
- High-quality protein and fats support muscle growth, satiety, and hormonal balance. Meat contains all essential amino acids, making it an optimal choice for muscle repair and maintenance. Animal fats promote satiety and play a crucial role in hormone regulation.
- This diet is rich in essential nutrients and ensures the body gets key vitamins and minerals. Meat supplies iron, B vitamins, and zinc, while fruit adds fiber, vitamin C, and antioxidants. Together, they create a nutrient-dense combination that supports immune function and recovery.
- Better digestion is one of the primary benefits of this approach. The meat is easy to digest and supports gut healing, while fruit balances the bowel movements and prevents digestive constipation. Most people who tend to bloat on high-fiber diets find that skipping complex foods makes gut health easier.
- Balanced energy levels make this diet ideal for the person who requires fuel with staying power. Fruit carbohydrates also give immediate energy, particularly for physical activity, and healthful fats ensure lasting satisfaction. Natural fruit sugars, in contrast to refined carbohydrates, do not trigger sudden drops in blood sugar levels.
- Another key benefit is reduced inflammation. By eliminating processed foods, seed oils, and grains, the body has a chance to heal from chronic inflammation. Many people report improvements in joint pain, skin conditions, and autoimmune symptoms after switching to a whole-food diet.
This diet is particularly effective for those looking to lose weight without extreme restrictions.
Many before and after results show significant fat loss and improved muscle definition.
Nutrient-dense foods and a natural balance between protein, fat, and carbs allow for steady progress, improved metabolism, and lower cholesterol levels over time.
RELATED: Amazing Carnivore Diet Before and After Transformations
Potential Drawbacks & Considerations
While the meat and fruit diet offers a balanced approach to nutrition, there are a few considerations to keep in mind.
Depending on individual metabolism, food choices, and overall health, some people may need adjustments to ensure long-term success.
- The insulin and blood sugar response will vary depending on the type and amount of fruit that is eaten. Some fruits contain more natural sugars, and this can lead to spikes in blood sugar, especially in those who are insulin-resistant or transitioning from a low-carbohydrate diet. It is helpful to note how different fruits affect energy and hunger levels to determine proper balance.
- Nutrient imbalance is likely to occur in the absence of variety in the diet. While meat provides essential protein and fats, it’s important that there are enough healthy fats like tallow, butter, or fatty meats to sustain energy over a long period. Those who rely too heavily on lean protein or excessive fruit intake can find themselves hungry or experiencing energy lows throughout the day.
Actionable Tip: The fruit selection is the most crucial for maintaining even energy levels and avoiding blood sugar dips. Consider the glycemic index, fiber, and fructose when selecting fruits to eat with meals. Slowly digested fruits provide sustained energy levels and suppress appetite.(3)
By exercising careful food selection and knowing the portion sizes, the meat and fruit diet can be tailored to suit any kind of health and fitness goals with few potential downsides.
Best Meats for the Meat and Fruit Diet
Choosing the right meats guarantees a balance of high-quality protein, healthy fats, and essential nutrients, creating a solid foundation for the meat and fruit diet.
Ruminant meats are some of the most nutritious foods, containing healthy quantities of iron, B vitamins, and zinc and making a person feel full.
They support muscles and provide sustained energy. Some of the best examples include:
- Beef
- Lamb
- Bison
- Venison
Poultry is a lean protein, so it is good for variety without losing the need for amino acids.
Some of these options are:
- Chicken
- Turkey
- Duck
- Wild game
Fatty fish and seafood are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which support brain health and reduce inflammation.
These options also provide iodine, an essential nutrient for thyroid function.
Consider adding:
- Salmon
- Sardines
- Shrimp
- Mackerel
Organ meats are some of the most nutrient-dense foods, supplying critical vitamins and minerals.
The liver is exceptionally high in vitamin A and iron. At the same time, bone marrow provides collagen and healthy fats that support joint and gut health.

Beneficial organ meats include:
- Liver
- Heart
- Bone marrow
- Kidney
For affordable consumers on the carnivore diet, cheaper cuts such as ground beef, chicken thighs, and organ meats offer the most nutrition without a significant expense.
Prioritizing nutrient-dense meats guarantees a balanced, effective, and sustainable meat and fruit diet.
What Fruits Can You Eat?
Choosing the right fruits can help maintain stable blood sugar, provide quick energy, and support digestion.(4)
The key is to focus on whole, nutrient-dense fruits while limiting those that may cause blood sugar spikes or digestive issues.
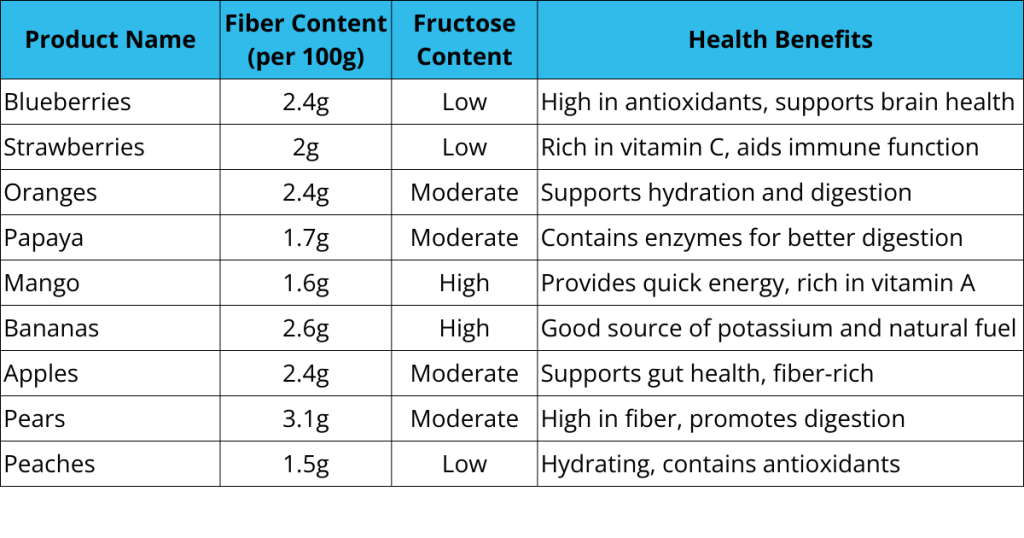
Fruits to Eat
Different fruits offer unique benefits based on their fiber and fructose content.
The table below highlights some of the best options to include in a balanced meat and fruit diet.
Fruits to Limit or Avoid
Some fruits contain high levels of natural sugars and should be eaten in moderation, especially for those managing blood sugar levels.
- Dried fruits like dates, figs, and raisins are nutrient-dense but highly concentrated in sugar, making them more likely to spike blood sugar.
- Certain tropical fruits, such as pineapple and watermelon, have a high glycemic index and may not be ideal for those watching their carb intake.
- Overly processed fruit products, such as fruit juices or canned fruits with added sugar, should be avoided, as they lack fiber and can cause insulin spikes.
Avocado is often debated on a meat and fruit diet. While technically a fruit, it is low in sugar and healthy fats, making it more similar to animal-based foods.
Some people include it in their diet, while others avoid it to maintain a stricter carnivore approach.
Choosing fiber-rich fruits in moderation ensures a balanced approach without unnecessary blood sugar fluctuations.
How to Structure Your Meals
Balancing protein, fat, and carbohydrates is key to making the meat and fruit diet work for your goals.
Adjusting your macronutrient intake allows for better results, whether aiming for fat loss, muscle gain, or sustained energy.
- Macronutrient balance depends on individual needs. Those focusing on fat loss may prioritize higher protein and moderate fruit intake. At the same time, those aiming for muscle growth can increase carbohydrates from fruit for energy. Healthy fats from meats and sources like ghee or tallow help maintain satiety and nutrient absorption.
- Meal timing plays a vital role in energy levels. Eating fruit before or after workouts can provide quick energy and improve recovery. At the same time, protein and fat-based meals help keep hunger in check throughout the day.
- Properly combining meat and fruit can avoid digestive issues. Some people experience bloating when consuming large amounts of fruit with fatty cuts of meat. Testing different combinations and portion sizes can help optimize digestion.
Sample Meal Plan
The meal plan below provides balanced ideas supporting energy, recovery, and digestion.
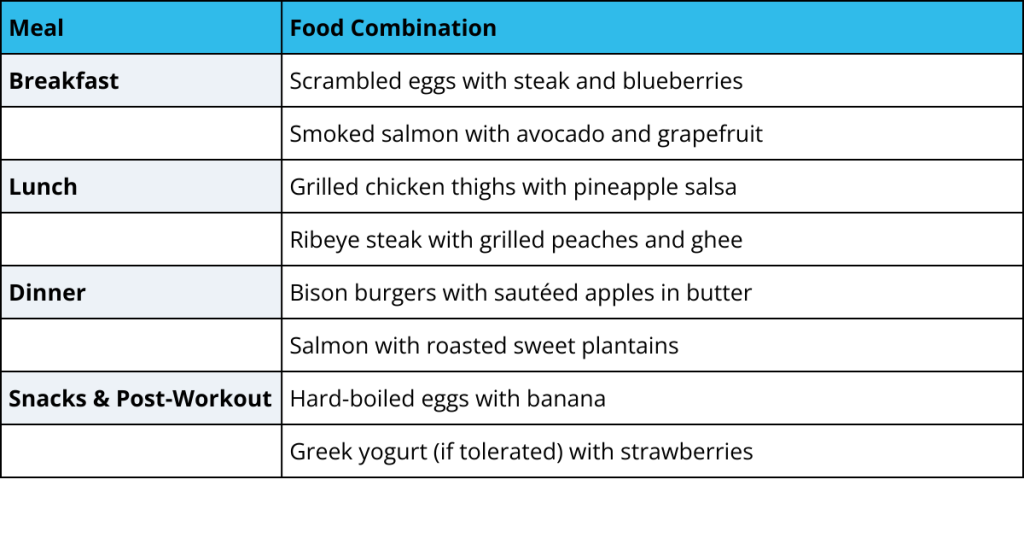
Some people also incorporate honey in small amounts for an extra energy boost, especially before workouts.
For snacks, keeping things simple with hard-boiled eggs, fruit, or Greek yogurt can help maintain energy levels between meals.
If eating out, focusing on fast food options like bunless burgers, grilled meats, and side fruit cups can help keep the diet on track.
For those looking for easy lunch ideas, pre-cooking meats and pairing them with fresh fruit makes meal prep simple and convenient.
Who Should Try the Meat and Fruit Diet?
The meat and fruit diet is a flexible, whole-food approach that works well for many people but may require adjustments for others.
Combining high-quality animal protein with nutrient-rich fruits offers a sustainable balance between low-carb and high-performance eating.
Best for:
- Athletes need whole-food carbohydrates for sustained energy, muscle recovery, and performance. Fruit’s natural sugars provide a quick fuel source without the processed additives in sports nutrition products.
- Those looking for a flexible alternative to strict carnivores but still want to keep their diet simple and whole-food-based. Adding fruit allows for more variety while maintaining the benefits of a meat-heavy diet.
- Keto and low-carb dieters who want to include strategic carb sources while staying away from grains and processed foods. The diet allows for natural carbohydrates without the insulin spikes associated with refined sugars.
May Need Modifications:
Individuals who are insulin-resistant or have blood sugar need to be cautious with their fruit consumption and stick to lower-glycemic fruits to avoid energy crashes or cravings.
- People on a very low ketogenic or zero-carb diet may find that consuming fruit kicks them out of ketosis. Adjust the serving size according to carb tolerance.
- Individuals with fruit sensitivities or histamine intolerance may need to experiment with different types of fruit to avoid digestive issues or allergic reactions.
The meat and fruit diet provides a structured yet adaptable way of eating, making it an excellent option for many people seeking better health, performance, and simplicity in their nutrition.
FAQ
Is the meat and fruit diet good for weight loss?
Ahh! Combining high-protein animal foods with fiber-rich fruits controls appetite and aids satiety, ensuring less overeating. The sugars in fruit provide a sustained amount of energy without the processed carb crashes. Such a diet has been said to cause many people to lose fat but maintain muscle.
Can you build muscle on a meat and fruit diet?
Absolutely! Meat provides complete protein with essential amino acids, while fruit supplies quick-digesting carbohydrates that fuel workouts and aid muscle recovery. The balance of protein and natural sugars supports strength, endurance, and muscle growth, making it an ideal diet for athletes and bodybuilders.
What’s the best fruit to eat on a meat and fruit diet?
Berries, bananas, citrus fruits, and melons are excellent choices due to their high nutrient density and lower levels of plant toxins. These fruits provide essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants while quickly digesting. Bananas and citrus fruits offer quick energy, while berries are rich in fiber and antioxidants.
Should I avoid certain fruits on this diet?
Certain people limit high-carbohydrate fruits like grapes and dates and nightshades like tomatoes and eggplant on the basis of their potential inflammatory impact. If you have sensitivities or gut issues, experiment with other fruits and observe which fruits are ideal for your body.
Can I eat this diet if I am keto or low-carb?
Yes! You may reduce fruit intake based on your carb tolerance if you need to opt for a lower-carb choice. Berries, citrus, and melons are excellent options for those who must limit their sugar but still benefit from some energy-dense carbs. The meat and fruit diet allows personalization based on personal requirements and goals.nd improved fat metabolism. By eliminating sugar and processed carbohydrates, the body efficiently burns stored fat for energy. However, results can vary bas
Final Thoughts
The meat and fruit diet is a simple, high-nutrient solution for fueling the body, gaining muscle, and increasing digestive function.
Obtaining good animal protein and natural sugar in the form of fruit meets the need for nutrients without processed foods or complex diets.
Its effectiveness leads many to choose energy nutrition, athletic performance enhancement, and adherence to body composition goals.
Keeping high-quality meats on top and selecting dense fruits appropriate for your needs is necessary.
Portioning modifications based on the activity level and personal needs ensures long-term maintenance of the diet.
For building muscle, reducing fat, or overall health, this dynamic diet can be adjusted according to various lifestyles.
This diet perfectly suits the lifestyle of people who do physical activities but, like any eating style, persona.






